Agentic AI adoption in network observability propels NetOps teams
Network observability is crucial for today’s networks and even more capable with agentic AI, according to new Omdia and BlueCat research.

As networks evolve and AI adoption becomes more widespread, network observability and intelligence have become crucial for keeping networks optimized and for identifying and resolving issues.
Most network monitoring tools will generate alerts when something is amiss. But they stop there, leaving resource-strapped network operations teams to figure out how to fix it. Network observability tools, meanwhile, correlate metrics, context, and configuration data to proactively detect and isolate root causes.
According to new research from Omdia, network observability tools are increasingly critical for modern networks. And vendors are rapidly adding AI to their toolsets, with significant promise for agentic AI.
Omdia’s 2026 report, Network Observability in the Agentic AI Era, reveals that AI technologies are reaching mainstream status for network observability. Slightly more than half of survey respondents are actively using agentic AI to boost capabilities.
In this post, we’ll first explore Omdia’s findings about why network observability—and not just monitoring—is critical for modern networks. Then we’ll look at survey results that demonstrate AI’s growing role in enhancing network observability for NetOps teams, particularly through agentic AI. And finally, we’ll touch on how BlueCat’s solutions can bring AI-powered observability to your network.

Network observability is essential for modern networks
To see what’s happening on their networks, network operations teams have traditionally relied on network monitoring tools. These tools collect telemetry, flows, and logs from as many devices and domains as possible. When something goes wrong, teams are flooded with alerts and dashboards that show something has happened.
But flagging that an issue exists is where most monitoring tools stop. Troubleshooting to resolve the issue can be reactive, manual, and slow. Teams pivot between dashboards, export data, and experienced guesses.
Network observability goes beyond traditional monitoring. It connects real-time metrics, network context, and configuration data to proactively detect and isolate the root causes of network issues. And it often resolves them before users even notice a problem.
Network observability answers more powerful questions: What is happening in the network, why is it happening, and what should we do next? Observability is not just about collecting data; it is about enabling understanding.
AI-powered applications make network observability more critical
As AI-powered applications move into broader adoption, network observability is even more critical, according to Omdia. Indeed, 90% of survey respondents strongly agree or agree that network observability is increasingly critical with the arrival of AI. Furthermore, 88% strongly agree or agree that AI technologies are essential for network observability.
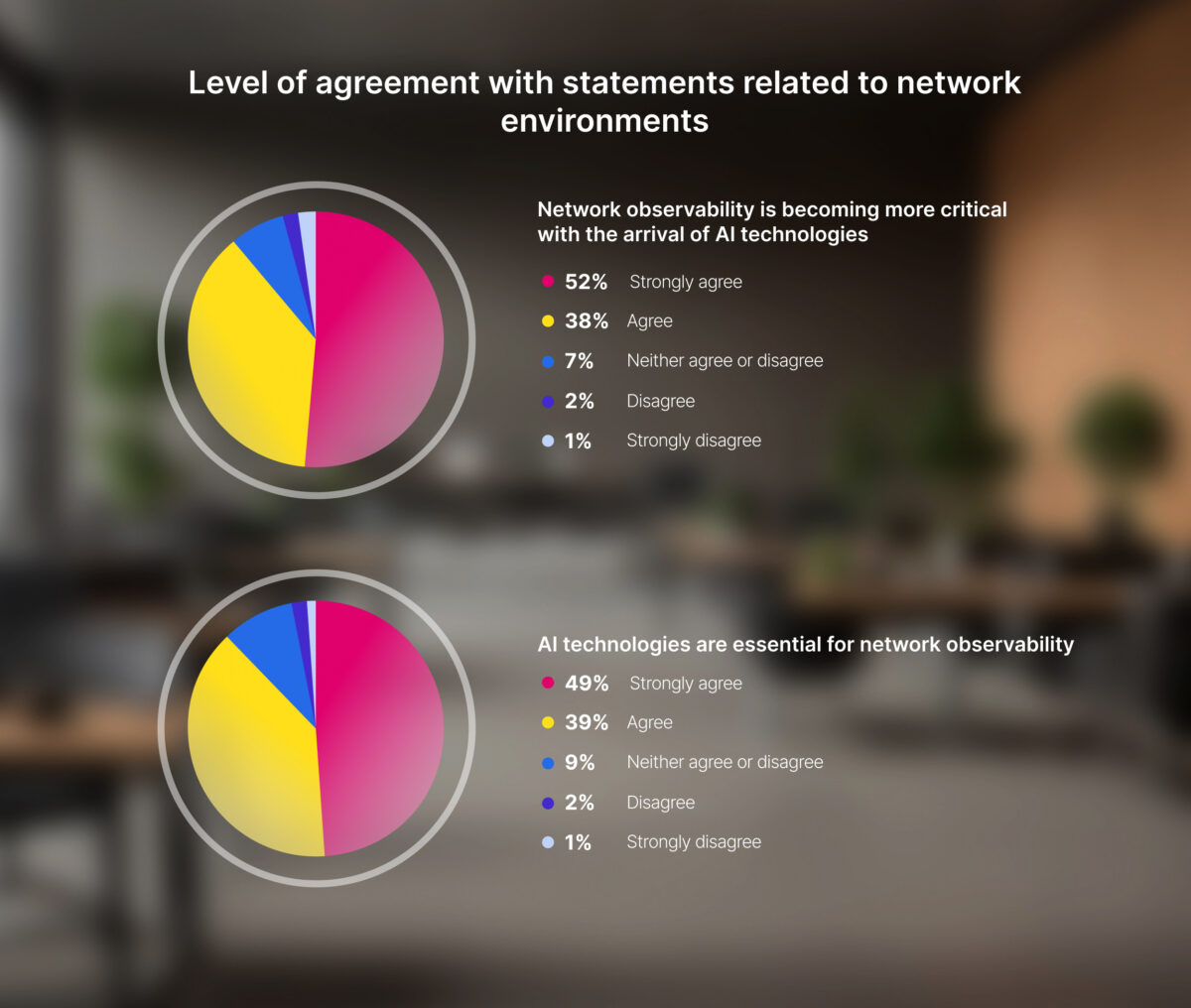
Survey respondents also indicated that the scope of network observability coverage is broad. Well over half of survey respondents report that their network observability efforts fully cover cloud networking, cloud access, data centers, and WAN. A broad range of data sources is also important, including system logs, user IDs, cloud flow logs, and IP address assignments.
Network observability has its challenges, too
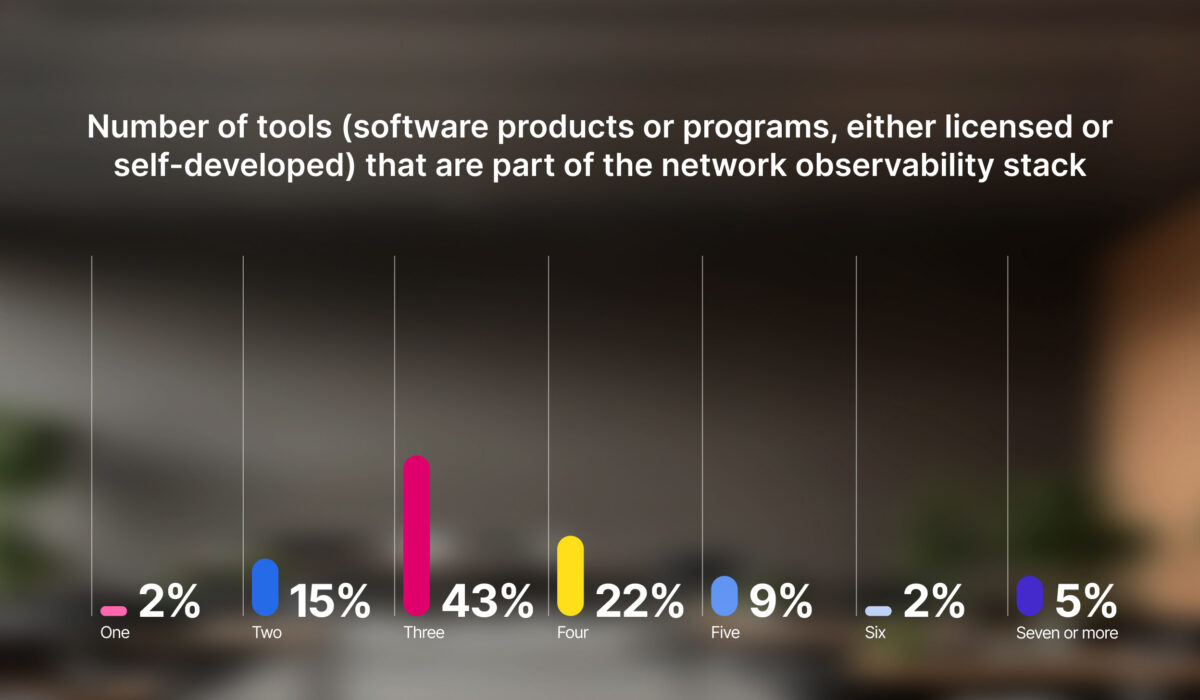
However, according to Omdia, network observability is not without challenges. Using fewer tools should lower costs and workloads. However, over 80% of respondents reported using three or more tools in their network observability stacks. Furthermore, integration is a major challenge for observability. Three-quarters of respondents identified integration between network tools or with observability frameworks as a top concern.
AI’s role in network observability is growing
The scale and complexity of modern networks make manual correlation for issue resolution no longer viable. No network engineer—no matter how experienced—can consistently connect the dots across performance telemetry, flow data, configuration state, and security signals in real time.
To keep up, network observability products are rapidly adding AI technologies. As a result, well over half of respondents reported that generative AI, machine learning, and agentic AI technologies are already used within or alongside their network observability tools. Among remaining respondents, near-universal adoption is expected over the next two years.
Accordingly, enterprises that are at the highest stage of network observability maturity leverage AI for prediction and optimization. According to Enterprise Management Associates, these enterprises use machine learning to forecast network behavior, capacity needs, and potential failures before they occur.
AI delivers a multitude of benefits for network observability
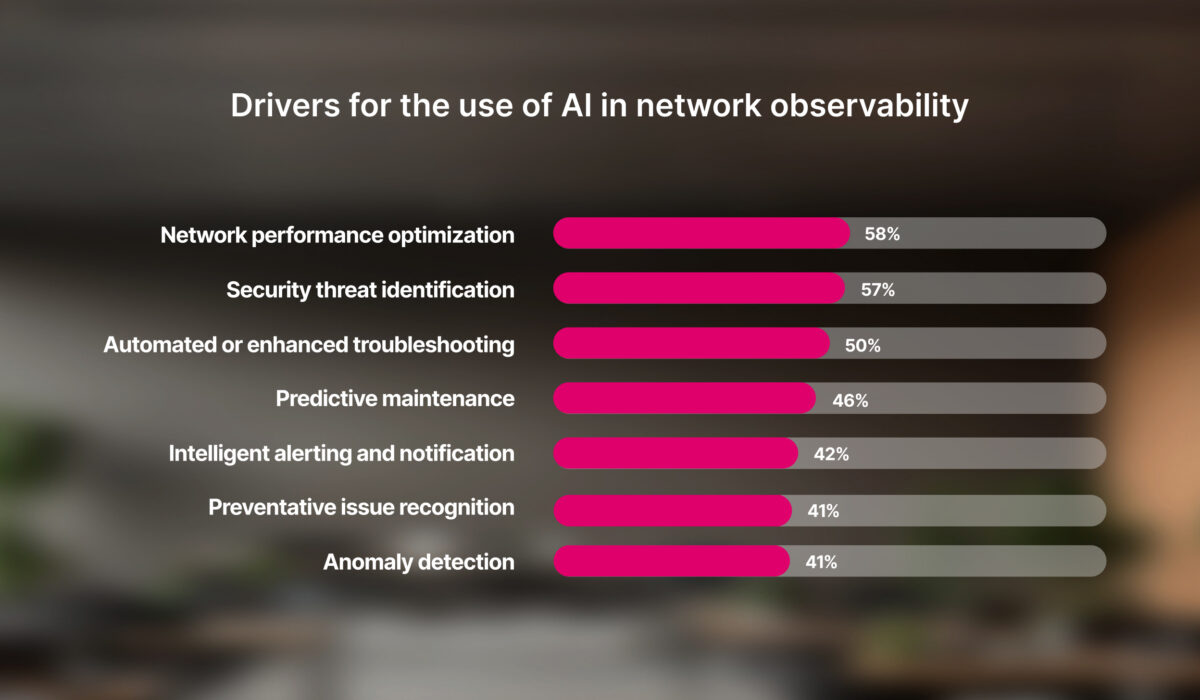
The potential drivers for using AI in network observability are numerous. According to Omdia, half or more than half of respondents see AI as enabling network performance optimization, security threat identification, or automated or enhanced troubleshooting. Other key uses identified include predictive maintenance, intelligent alerting notification, preventative issue recognition, and anomaly detection.
Furthermore, Omdia’s research found that AI is meeting or exceeding expectations among most organizations across all surveyed use cases. For example, AI’s performance in security threat identification exceeded expectations for 64% of respondents and met expectations for another 28%.
Agentic AI is gaining traction for network observability
Among survey respondents using generative AI for network observability, well over half use it for knowledge capture and preservation, knowledge base access, and conversational network analysis.
But agentic AI, which acts autonomously, using tools and reasoning to solve problems and execute multi-step tasks, is also beginning to directly impact network observability.
Agentic AI can conduct autonomous activities and take proactive measures. Much of this is beyond the practical reach of resource-strapped network operations and engineering teams. Indeed, 86% of respondents strongly agree or agree that agentic AI can help close network observability skill gaps.
Just over half of respondents reported using autonomous monitoring and analysis. Another 42% reported that it is in the process of deployment. Another 48% are using agentic AI for support for autonomous workflows, while 36% intend to deploy it in the future. Other common agentic AI applications reported include continuous policy compliance assessment, continuous network discovery, and recommended action plans.

AI-powered network observability solutions are here
BlueCat’s network observability and intelligence solutions continuously capture and visualize a broad range of telemetry across the whole network for more actionable insights, including:
- Flow data, API, SNMP, and cloud telemetry for performance monitoring
- Packet data for enterprise-wide network forensics
- Configuration data to detect and remediate issues across DNS, DHCP, and IP address management (together known as DDI) services, firewalls, and load balancers
Furthermore, LiveAssist, an AI-powered add-on to LiveNX, BlueCat’s network observability solution, helps NetOps teams gain real-time network insights and guided issue remediation. With agentic AI capabilities, LiveAssist doesn’t just summarize data; it thinks and acts like an experienced network engineer. It understands multi-vendor telemetry from flows, SNMP, APIs, and packets, and automatically correlates symptoms to causes. And it recommends next steps, all through a natural language interface.
Ready to learn more about network observability and how agentic AI is transforming it? Download Omdia’s full Network Observability in the Agentic AI Era report today.




