Make Point of Sale security a reality with DNS
Point-of-Sale systems are used to process a ton of customer transactions. But what happens when convenience gets in the way of security?

You may not be intimately familiar with Point of Sale (POS) systems but unless you’ve been living under a rock, you’ve definitely used them. They’re everywhere these days – from older cash register look alikes to hot new mobile POS card readers tethered to mobile phones. See something you like? Swipe, tap or PIN away, and you own it.
But are you confident your credit card details aren’t being shared?
Unfortunately, POS security is a real challenge, because these payment systems are a favorite target of hackers, and account for 90% of the data breaches seen in the industry according to Verizon’s DBIR 2018 report. The drive behind this is the demand on the black market for credit card data, with active numbers fetching $1 to $3 or more apiece. For example, the now infamous Target breach in 2013 affected 40 million customer debit and credit card accounts – a staggering amount. Network teams must do more to protect customers.
Point-of-sale system are rather straightforward. They collect customer data and apply updates. The information collected by terminals is incredibly sensitive, and deserves appropriate data protection. Sensitive customer information like names, addresses, contact information and of course credit card information is routinely processed with every transaction. This is often referred to as Track 1 and Track 2 data. Several times a day, updates are pushed down to the terminals on things like inventory levels, pricing and promotions.

The systems are secured – for the most part – and governed by the Payment Card Industry (PCI) which sets the Data Security Standard (DSS). These standards require the use of things like using a firewall, encrypting sensitive data in transit across open, public networks, using regularly-updated anti-malware solutions. The list goes on.
But hackers have found a loophole.
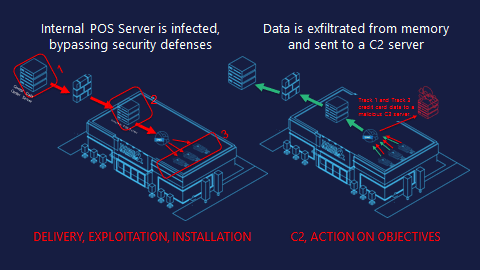
They target the most vulnerable point of the POS – on the terminal as it’s batching payments for processing. This procedure is done in-memory on the device before it’s encrypted and sent to internal servers for processing. Using a small window, RAM scrapers can gain access, infected the terminal and harvest this payment data to send it off to the adversary’s remote Command & Control (C2) server.
THE ATTACK
Here’s how it works.
First RAM scrapers bypass external defenses such as a firewall or IDS using run-of-the-mill methods like social engineering, phishing. Sometimes they use embedded links in vulnerability exploits that are often disclosed and patched every month by the PoS vendors themselves. Once inside, they infect the central POS servers to push down a malicious update to the terminals.
It’s a real cat-and-mouse game.
Once the malicious RAM scraper has infected the terminal, it targets the clear-text credit card data, collects the data and begins processing it. In the majority of these cases this process includes packaging the data using Base64 encoding, or another format, and chunking it into packets of weird strings appended to the front of a URL. It then sends this data over DNS to a malicious server for collection.
How BlueCat DNS Edge Helps
DNS security to the rescue.
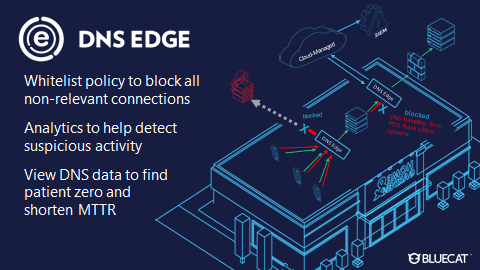
DNS Edge, the cornerstone of BlueCat’s intelligent security offerings, helps network security to prevent these exploits.
First, it allows teams to set whitelist policies that automatically block all non-relevant connections. These are like “single-lane highways with no exits” between the POS devices and the terminals during a transaction. If a POS terminal attempts to go outside that narrow list of whitelisted domains, it can be blocked or monitored.
For example, If a POS device is trying to reach google.com, that’s a problem. Visiting Google.com is outside the device’s normal function, so it indicates there’s a compromise and that terminal needs to be ripped out of the wall.
DNS Edge service points elsewhere on your network (for example, placed behind your internal PoS Server) can help analyze all DNS queries and identify patterns of malicious activity like tunneling or any DGAs. Adversaries are known to attempt data exfiltration from multiple spots.
Reviewing DNS data in the DNS Edge console to look at violated block and monitor policies, in addition to malicious patterns detected by its smart analytics, can help shorten mean-time-to-repair and identify patient zero.
DNS is a powerful protocol that adversaries have been exploiting maliciously for many years as it’s often been unmonitored by most organizations.
How This Works in Edge
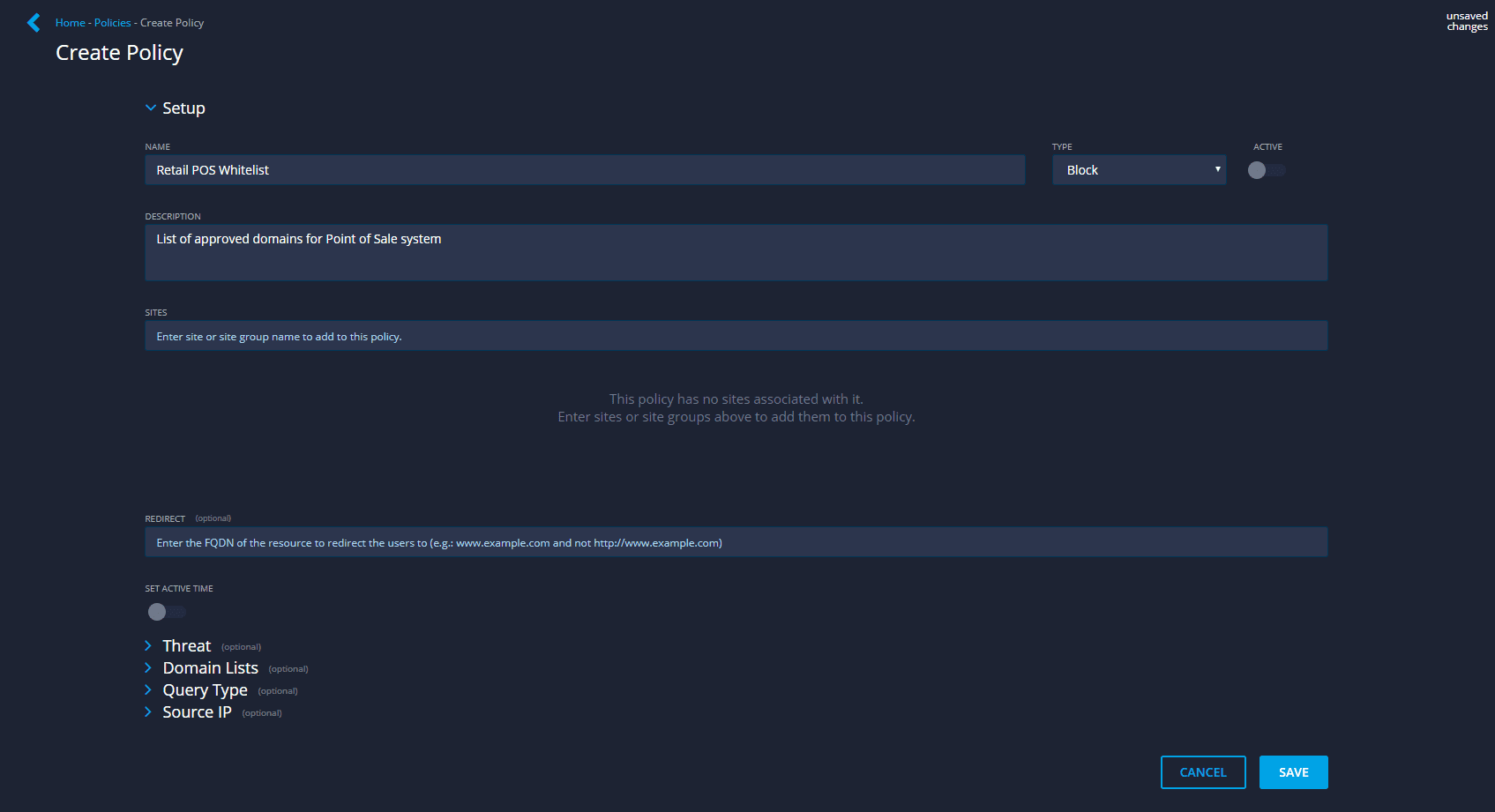
Create a policy in Edge to whitelist only the on-network services and domains point-of-sale terminals are allowed to speak to.
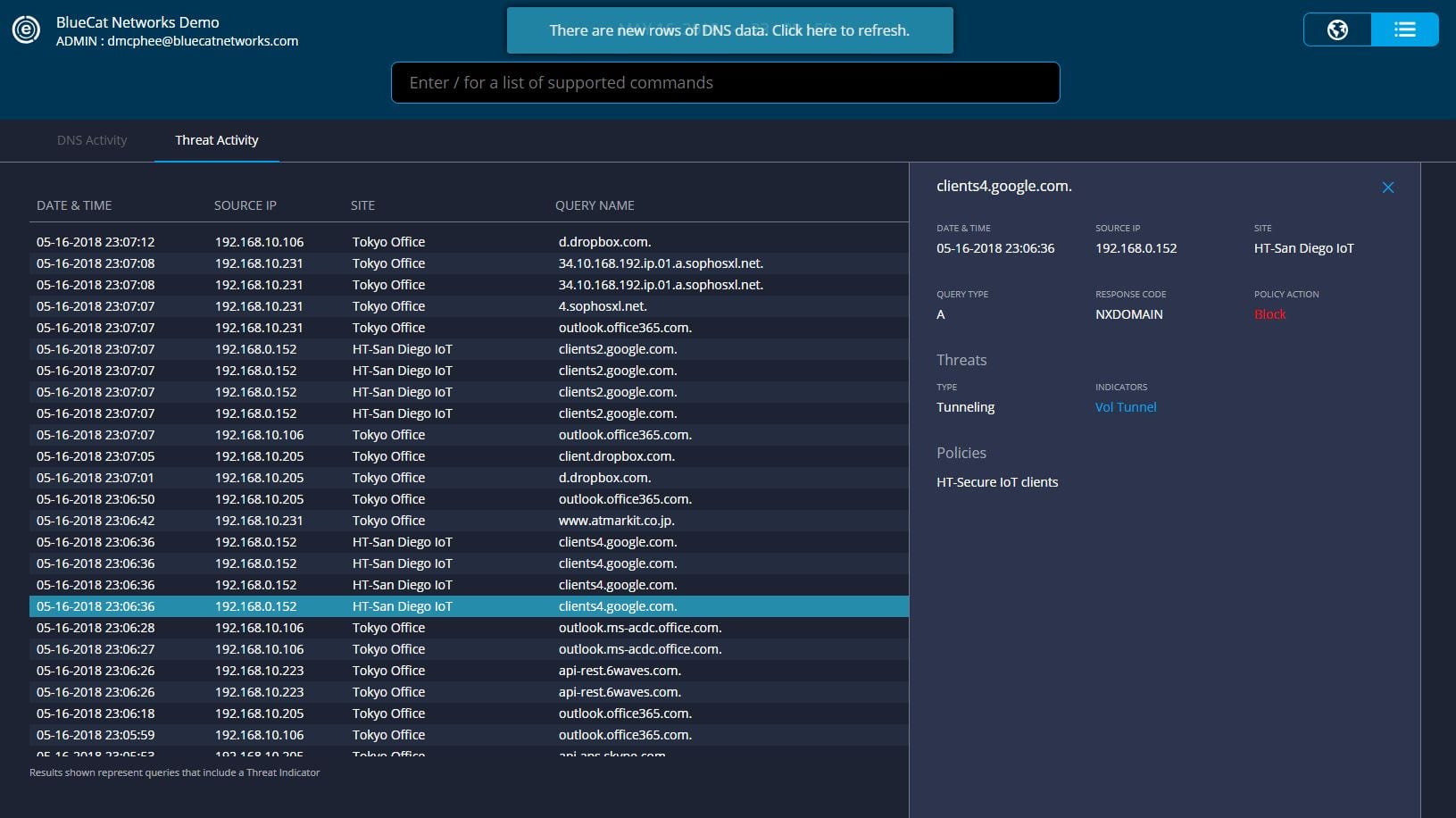
Attempts to reach any domains outside of the allowed list are blocked.
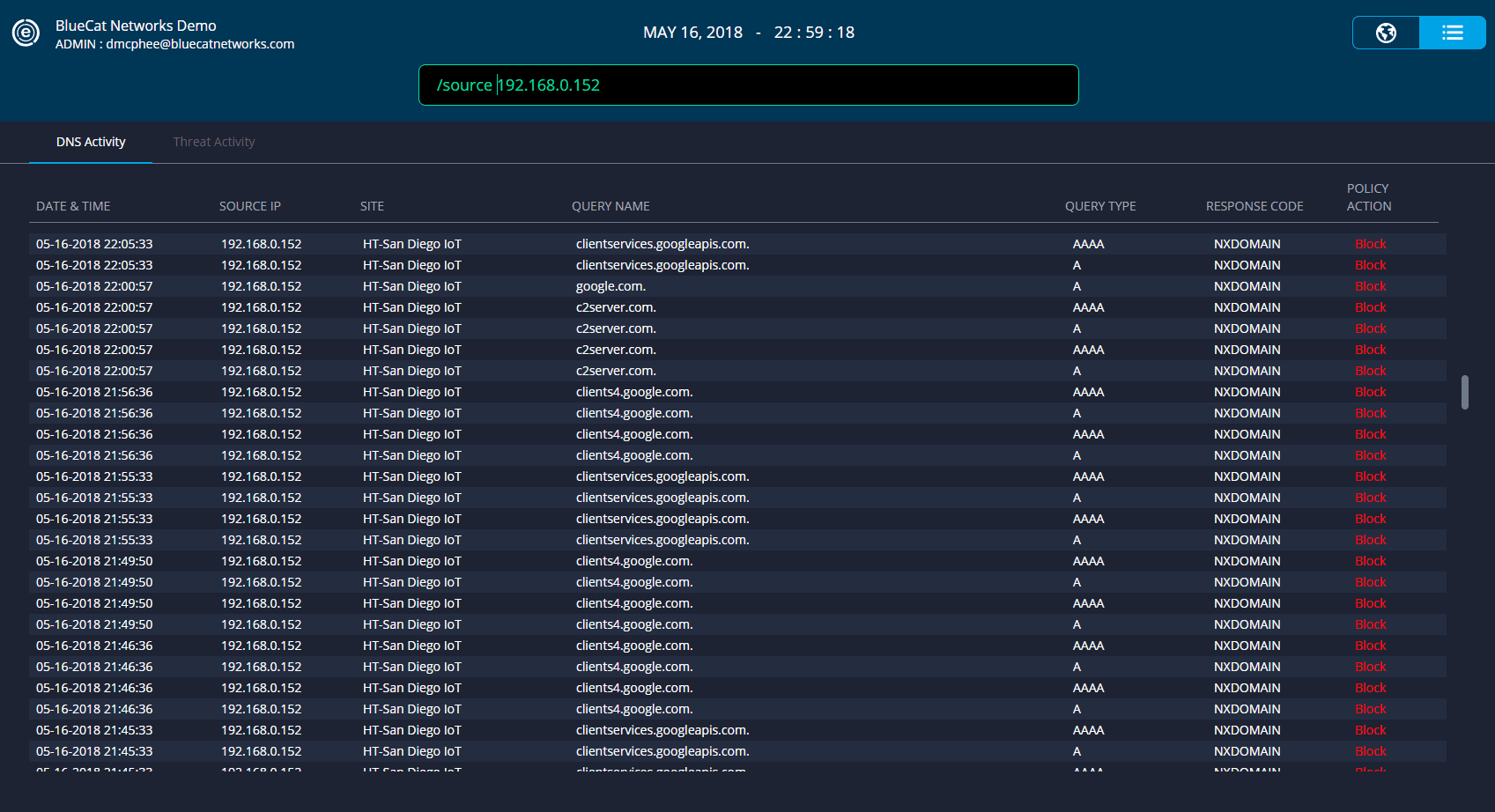
Review blocked query attempts within Edge and the originating host to identify potentially compromised PoS devices.